Argon Gas WindowsWhat is Argon Gas and what does it do?
-

What is Argon
Air thicker than oxygen
- Quieter than air between the panes due to density of Argon Gas
- Prevents heat infiltration. slows conduction and convection of heat and cold through the window glass.
- Slows conductivity thereby slowing condensation.
- Slows convection by providing lower U Values and better performance than typical double paned window glass.
Argon Gas in Replacement Windows
What does Argon do to a residential glass package?
-
Argon Gas Report Data related to humidity, condensation, air infiltration, conduction and convection in residential windows
-
-
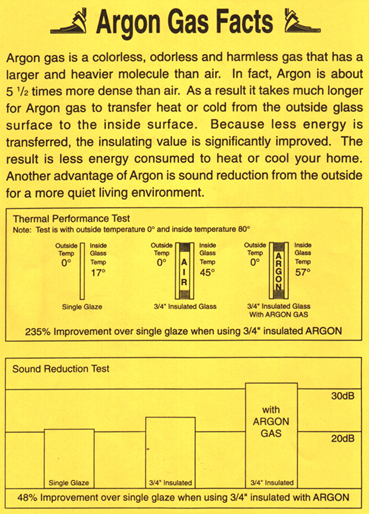
Argon gas is an innert gas that is 5 times denser than oxygen.
Correspondingly sound and temperature are slower to move through argon than through regular air. It dampens sound and temperature conductivtity.
-
From the Greek word argos (inactive)
Atomic Number: 18
Atomic Mass: 39.948
Thermal Conductance: 47.87% LOWER than air
BTU over hour foot degree F: [(.0139-.0094)/.0094]
Density: 38.01% MORE DENSE than air
Pounds per cubic foot: [(.1111-.0805)/.0805]
Viscosity: 22.16%MORE VISCOUS than air
Argon's high density allows it to remain in an open container with little or no diffusion of oxygen or nitrogen into it. Because of this, argon is easily contained between sealed and tilted dual panes of glass until the filling holes are plugged. It sits inside its insulating glass container like a glass filled with water, until the filling hole or vent hole is properly sealed to complete the insulating glass unit.
Discovered in 1894 by Lord Rayleigh and Sir William Ramsey, argon's presence in air was suspected by Cavendish in 1785 because after removing all traces of oxygen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, moisture, and dust particulates from the air, there was still some gas present.
Argon forms 0.934% of Earth's atmosphere, making it the most common of the so-called "noble" or "inert gases". Argon is recovered by fractional distillation from air. Colorless, tasteless and odorless, argon is a true inert gas, not forming true chemical compounds as do the other noble gases (helium, neon, krypton and xenon). It is about twice as soluble in water as nitrogen. Argon is also used to exclude nitrogen and oxygen from contact with metals during welding or a process that would be adversely affected by the presence of normal atmospheric gases.
Beyond improving the thermal performance of insulating glass by reducing conductance between the panes, argon is used in gas-filled electric light bulbs, radio tubes, and Geiger counters, and in the production and fabrication of metals such as titanium, zirconium, and uranium. Argon is also used for growing crystals of semi-conductors, such as silicone and germanium.
Insulating glass is the "critical ingredient" of any residential window system. Window manufacturers use high-grade sealants and expensive equipment to glue the perimeter of two or more panes of glass together. This hermetic seal is accomplished to form a "dead air space" of a specific dimension between the panes. The optimum space between the two panes is around 9/16", or .5625". Depending on the thickness of the glass panes used, which varies depending upon window size, the overall glass thickness with this optimum airspace will be around ¾" or .750". This is typical of PPG, Cardinal Glass or Guardian Glass. The three primary manufacturers of glass products.
Desiccants, a purer form of zeolite-based drying agent than you might find in a packet inside a new shoe or camera box for example, are a part of the sealant system and work to "dry up" any humidity trapped between the panes during assembly in the factory. The resulting dry, dead air space works remarkably well to insulate the inner pane from the outer pane of glass. The result is a better-insulating window than single pane windows for lower energy use, cooler summers and warmer winters.
Over time, technical experts in the business determined that carefully selected materials in the sealant system reduce condensation around the perimeter of the insulating glass unit of a window ("warm edge spacer"). They also discovered complex coatings on the glass that reflect and re-direct the sun's rays and its energy (low-emissivity glass). At about the same time, somebody wondered what would happen to the thermal resistance of the dead air space if we used something heavier, something "more dead" than a "dead air space". The search included some exotic gases, gels, and even certain liquids. Of all the possibilities, the most popular choice has been argon gas. Argon is by far the most popular material for this use, due to its abundance and availability, low cost, clarity, low conductance, high density, and because it is generally safe to use. -
Krypton Gas is actually heavier but about three times the cost overall of Argon and it requires a smaller dead air space that's created with a triple glazed replacement window. Krypton with Triple Glazing will add about $250 to the cost of a mid ranged vinyl replacement window quickly moving it to the high end range.